Centralized cloud storage revolutionizes data management by consolidating vault resources in a single, remote location accessible over the internet. This paradigm shift allows organizations to store vast amounts of data securely and efficiently without the need for on-premises hardware infrastructure. Leveraging offers unparalleled scalability, enabling businesses to effortlessly scale their storage capacity up or down as needed, thereby optimizing resource utilization and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the concentrate nature of cloud storage streamlines data management processes, providing concentrate control and visibility over stored data assets. This enhanced manageability empowers organizations to streamline data provisioning, backup, and recovery operations, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and agility. In essence, it serves as the cornerstone of modern data management strategies, enabling businesses to unlock the full potential of their data assets while driving innovation and growth.
Overview of Centralized Cloud Storage
Centralized cloud storage represents a paradigm shift in data management, facilitating seamless access to data resources through remote servers managed by third-party providers. This innovative approach eliminates the need for physical storage infrastructure, enabling organizations to leverage scalable and flexible storage solutions tailored to their needs. By centralizing data storage, businesses can optimize resource utilization and streamline operations, unlocking new levels of efficiency and productivity. The concentrate nature of cloud storage empowers organizations to consolidate their data assets, simplify management processes, and improve accessibility across distributed teams and locations.
Importance of Data Storage Solutions
Understanding Centralized Cloud Storage
Centralized cloud storage entails storing data on remote servers managed by third-party providers. This approach eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure, facilitating data access and management via the internet. In essence, it centralizes data storage in a single location, enabling authorized users to access data from anywhere globally. The infrastructure of centralized cloud storage comprises essential components like data centers, servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. Data centers serve as the foundation, housing servers and storage devices that securely store and manage data. Networking equipment facilitates data transmission between servers and users, ensuring seamless access to stored data.
Definition and Concept
Centralized cloud storage, at its core, involves the vault of data on remote servers managed by third-party providers. This approach eliminates the need for on-premises hardware and infrastructure, allowing organizations to access and manage their data via the internet. In essence, centralized cloud storage operates on the principle of centralization, where data is stored in a single, centralized location, accessible to authorized users from anywhere in the world.
Key Components and Infrastructure
The infrastructure of centralized cloud storage comprises several key components, including data centers, servers, vault devices, and networking equipment. Data centers serve as the backbone of the storage infrastructure, housing servers and storage devices that store and manage data. These servers are equipped with storage drives, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs), which store the data securely. Networking equipment, including routers, switches, and cables, facilitate data transmission between servers and users.
How Centralized Cloud Storage Works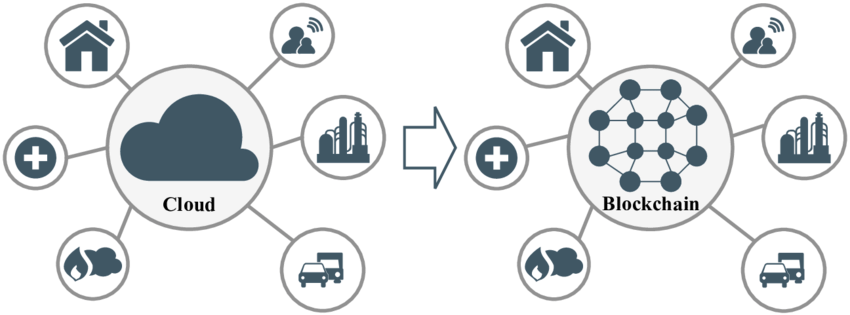
Centralized cloud storage operates on a client-server model, where clients (users or applications) access data stored on remote servers via the internet. When a user or application requests access to data, the request is sent to the centralized cloud storage provider’s servers. The servers retrieve the requested data from the storage devices and transmit it back to the user or application over the network. This process ensures seamless and efficient access to data, regardless of the user’s location or device.
Advantages of Centralized Cloud Storage
It, presents several challenges that organizations must navigate to ensure the security, privacy, and reliability of their data. Security concerns are paramount, as storing sensitive information on remote servers increases the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Compliance with data privacy regulations adds another layer of complexity, requiring businesses to navigate a labyrinth of legal requirements to safeguard customer data. Additionally, the reliance on a single point of failure in centralized cloud storage architectures leaves organizations vulnerable to disruptions and downtime. Performance issues, such as latency and bandwidth constraints, further compound these challenges, impacting user productivity and application responsiveness.
Security Concerns
One of the foremost challenges of centralized cloud storage revolves around security concerns. Storing sensitive data on remote servers managed by third-party providers raises apprehensions regarding data breaches, unauthorized access, and cyber threats. Organizations must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and multi-factor authentication, to mitigate these risks and safeguard their data integrity.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Maintaining data privacy and compliance with regulatory requirements poses another significant challenge for the users. With data sovereignty laws and regulations becoming increasingly stringent, businesses must ensure that their data stored in centralized cloud environments complies with relevant legislation, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in severe penalties and reputational damage. You can also, Discover how DePIN integrates with centralized cloud storage to revolutionize infrastructure management. Learn more here.
Single Point of Failure
It, introduces the risk of a single point of failure, where a disruption or outage in the cloud infrastructure can lead to widespread data loss or downtime. Organizations must implement robust redundancy and failover mechanisms to mitigate this risk and ensure business continuity. Distributed storage architectures and geographically dispersed data centers can help minimize the impact of potential failures.
Performance Issues
Performance issues, such as latency and bandwidth constraints, can arise in its environments, particularly during peak usage periods or when accessing data from remote locations. These performance bottlenecks can hamper user productivity and affect application performance. To address these challenges, organizations may need to optimize their network infrastructure, implement caching mechanisms, or leverage content delivery networks (CDNs) to improve data access speeds and responsiveness.

 China
China Russia
Russia India
India










